Position Sizing: How Much Should You Really Invest? A Complete Guide to Smart Trade Management
Master position sizing strategies used by professional traders. Learn fixed-percentage, volatility-based, and portfolio-based methods to optimize your trade size and risk management.
The Most Critical Yet Overlooked Trading Decision
Position sizing is arguably the most important decision a trader makes, yet it's often reduced to oversimplified rules like "risk 2% per trade." While such guidelines provide a starting point, professional traders understand that effective position sizing is a dynamic process that considers multiple factors beyond basic percentage rules.
Why Position Sizing Makes or Breaks Traders
The impact of position sizing on trading success cannot be overstated. Consider these revealing statistics:
- Traders who practice proper position sizing have an average drawdown of 20-30%
- Aggressive position sizing can lead to drawdowns exceeding 50%
- Professional traders rarely risk more than 1-2% per trade
- Most blown trading accounts result from improper position sizing
Understanding these statistics helps explain why even profitable strategies can fail when combined with poor position sizing decisions.
Core Position Sizing Methods
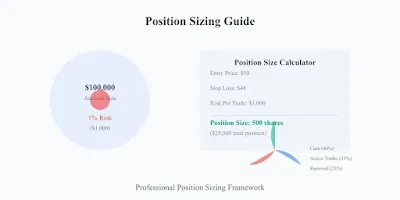
1. Fixed Percentage Risk Method
The fixed percentage approach forms the foundation of basic position sizing. This method ensures consistent risk exposure across trades regardless of entry price or stop distance.
Calculation Formula:
Position Size = (Account Size × Risk Percentage) ÷ (Entry Price - Stop Price)
Example:
- Account size: ₹5,00,000
- Risk per trade: 1% (₹5,000)
- Entry price: ₹100
- Stop price: ₹95
- Position size = ₹5,000 ÷ ₹5 = 1,000 shares
Advantages:
- Simple to calculate
- Consistent risk exposure
- Easy to track and adjust
- Suitable for beginners
Limitations:
- Doesn't account for market volatility
- May not optimize for different setups
- Ignores correlation risks
- Doesn't consider overall portfolio exposure
- Account size: ₹5,00,000
- Risk amount: ₹5,000
- Current ATR: ₹2
- ATR multiple: 3
- Position size = ₹5,000 ÷ (₹2 × 3) = 833 shares
- Adapts to market conditions
- Provides dynamic risk adjustment
- Reduces whipsaws in volatile markets
- Optimizes for market conditions
- Portfolio value: ₹10,00,000
- Maximum heat: 20%
- Correlated positions: 4
- Maximum position heat = (₹10,00,000 × 0.20) ÷ 4 = ₹50,000 per correlated position
- Can handle larger positions
- Lower impact costs
- Higher liquidity
- Faster execution
- Moderate position sizes
- Consider liquidity constraints
- Monitor impact costs
- Stage entries and exits
- Smaller positions
- Significant liquidity premium
- Higher impact costs
- Careful entry/exit planning
- Maximum 1% of average daily volume
- Consider position exit time
- Account for market impact
- Plan for emergency exits
- Full position size (1-2% risk)
- Clear technical alignment
- Strong fundamental backing
- Optimal market conditions
- Half position size (0.5-1% risk)
- Good but not optimal setup
- Mixed technical signals
- Normal market conditions
- Quarter position size (0.25-0.5% risk)
- Speculative opportunity
- Unclear technical picture
- Challenging market conditions
- Normal position sizing
- Full risk per trade
- Standard setup evaluation
- Regular portfolio heat
- 80% of normal size
- Increased scrutiny of setups
- Reduced portfolio heat
- Focus on A+ setups
- 50% of normal size
- Only A+ setups
- Minimal portfolio heat
- Consider trading break
- Standard position sizing
- Regular risk per trade
- Normal setup evaluation
- Full portfolio exposure
- Reduced position sizes
- Lower risk per trade
- Higher setup standards
- Decreased exposure
- Minimal position sizes
- Reduced risk per trade
- Only best setups
- Limited exposure
- Calculate basic position size
- Adjust for volatility
- Check volume constraints
- Consider portfolio heat
- Evaluate market conditions
- Assess setup quality
- Final size determination
- Basic position size
- Volatility adjustments
- Portfolio heat tracking
- Drawdown monitoring
- Real-time calculations
- Multiple method support
- Portfolio analysis
- Risk monitoring
- Ignoring transaction costs
- Overlooking liquidity constraints
- Miscalculating total risk
- Forgetting correlation effects
- Increasing size after wins
- Doubling down on losses
- Ignoring system signals
- Emotional position scaling
- Maximum 3 entry points
- Each entry requires its own stop
- Total risk stays within limits
- Clear scaling criteria
2. Volatility-Based Position Sizing
This advanced method adjusts position size based on market volatility, typically using Average True Range (ATR) as a measure.
Calculation Formula:
Position Size = (Account Risk) ÷ (ATR × ATR Multiple)
Implementation Example:
Benefits:
3. Portfolio Heat Method
This sophisticated approach considers total portfolio exposure and correlation between positions.
Formula:
Maximum Position Heat = (Portfolio Value × Max Heat %) ÷ Number of Correlated Positions
Example Implementation:
Advanced Position Sizing Considerations
1. Market Capitalization Adjustments
Position sizes should be adjusted based on the market capitalization of the traded instrument:
Large-Cap Stocks:
Mid-Cap Stocks:
Small-Cap Stocks:
2. Volume-Based Position Sizing
This method considers trading volume to ensure positions can be entered and exited efficiently.
Guidelines:
Formula:
Maximum Position = Average Daily Volume × 0.01
3. Risk Multiple Position Sizing
This approach varies position size based on setup quality:
A+ Setup:
B Setup:
C Setup:
Dynamic Position Sizing Factors
1. Account Drawdown Adjustments
Modify position sizes based on account performance:
Peak Equity:
5% Drawdown:
10% Drawdown:
2. Market Regime Considerations
Adapt position sizing to market conditions:
Bull Market:
Sideways Market:
Bear Market:
Implementation Framework
1. Position Sizing Worksheet
Create a systematic approach:
Pre-Trade Checklist:
2. Position Sizing Tools
Essential calculators and tools:
Risk Calculator:
Position Sizing Software:
Common Position Sizing Mistakes
1. Technical Errors
Common pitfalls to avoid:
2. Psychological Mistakes
Mental traps to watch for:
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Should position size change with account growth?
Yes, You can do it if you want. But incrementally. Increase position sizes by 25% when account grows by 50% from starting value.
Q: How does leverage affect position sizing?
Leverage should not increase your effective risk. Calculate position size based on actual account equity, not leveraged buying power.
Q: What about scaling into positions?
Scale-in rules:
Q: How to handle correlated positions?
Treat correlated positions as a single trade for risk purposes. Divide total risk among correlated positions.
Conclusion: Building Your Position Sizing System
Effective position sizing combines mathematical precision with practical market wisdom. Start with basic percentage risk, then gradually incorporate more sophisticated methods as your trading evolves. Remember that position sizing is not static – it should adapt to market conditions, account performance, and setup quality.
The key to successful position sizing lies in consistency and discipline. Develop your system, test it thoroughly, and stick to it through both winning and losing periods. Regular review and adjustment of your position sizing rules ensure they remain effective as markets and your trading evolve.









0 Comments