What is Divergence in Stock Charts? A Clear Explanation
Divergence is a popular concept in technical analysis that traders use to identify potential market trends. When the value of something goes the opposite way of a technical indicator, that's what we call it. When this happens, it is believed that the current price trend is weakening, and a reversal may be approaching.
Understanding divergence is essential for traders to identify potential trading opportunities. There are two types of divergence: positive and negative. Positive divergence occurs when an indicator starts moving higher after prices have been in a downtrend, while negative divergence happens when an indicator starts moving lower after prices have been in an uptrend.
Traders use divergence to read momentum and signals of weaker price trends. However, there are limitations to divergence analysis, and traders must be aware of them. In this article, we will discuss what divergence is, how to identify it, and how to use it in trading strategies.
Key Takeaways
- Divergence occurs when the price of an asset moves in the opposite direction of a technical indicator, indicating a potential weakening of the current price trend.
- Positive divergence happens when an indicator starts moving higher after prices have been in a downtrend, while negative divergence happens when an indicator starts moving lower after prices have been in an uptrend.
- Divergence is a useful tool for traders to identify potential trading opportunities, but it has limitations that traders must be aware of.
Understanding Divergence
Definition of Divergence
Divergence is a technical analysis tool that helps traders to identify potential trend reversals in the market. When a technical indicator suggests one thing, but the price of an asset decides to do the opposite, that's what we mean by a divergence. In other words, it is a disagreement between the price action and the technical indicator. Positive or negative divergence happens when the relationship between a technical indicator and the price of an asset goes in favor of the indicator (positive) or against it (negative).
Positive divergence occurs when the price of an asset is moving in a downtrend, but the technical indicator is moving in an uptrend. This suggests that the price may soon reverse and start to move upwards. On the other hand, negative divergence occurs when the price of an asset is moving in an uptrend, but the technical indicator is moving in a downtrend. This suggests that the price may soon reverse and start to move downwards.
Types of Divergence
Divergence comes in two types: regular and hidden. Regular divergence occurs when the price of an asset is moving in the opposite direction of a technical indicator, while hidden divergence occurs when the price of an asset is moving in the same direction as a technical indicator, but the indicator is not confirming the price action.
Regular divergence can be either positive or negative, while hidden divergence can only be positive. Regular positive divergence occurs when the price of an asset is making a lower low, but the technical indicator is making a higher low. Regular negative divergence occurs when the price of an asset is making a higher high, but the technical indicator is making a lower high.
Significance in Technical Analysis
Divergence is a powerful tool in technical analysis as it can help traders to identify potential trend reversals in the market. It can be used in combination with other technical analysis tools to confirm trading signals. However, it is important to note that divergence is not a perfect tool and should not be relied on solely to make trading decisions. Traders should always use other technical analysis tools and fundamental analysis to confirm trading signals and make informed decisions.
Indicators of Divergence
When it comes to identifying divergence in stock charts, there are several indicators that traders can use. These indicators can help traders spot potential trend reversals and make more informed trading decisions. In this section, we will discuss three of the most commonly used indicators of divergence: Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Stochastic Oscillator.
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) is a popular indicator used to identify trend reversals. It is calculated by subtracting the 26-period exponential moving average (EMA) from the 12-period EMA. The result is then plotted on a chart as a line, known as the MACD line.
When the MACD line crosses above the signal line (a 9-period EMA of the MACD line), it is considered a bullish signal. On the flip side, if the MACD line goes down and crosses under the signal line, that's a sign that things might turn bearish. Divergence occurs when the MACD line and the price of the asset being traded move in opposite directions. This could indicate a possible shift in the trend, suggesting that the current direction might be about to change.
Relative Strength Index (RSI)
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is another popular indicator used to identify divergence. It measures the strength of an asset's price action by comparing the average gains and losses over a specified period of time. The RSI is plotted on a chart as a line that oscillates between 0 and 100.
If the RSI goes beyond 70, it's seen as overbought, suggesting the asset might be overvalued. Conversely, if it drops below 30, it's deemed oversold, hinting that the asset may be undervalued. Divergence occurs when the RSI and the price of the asset being traded move in opposite directions. This could indicate a possible reversal in the trend, suggesting that the current direction might be about to change.
Stochastic Oscillator
The Stochastic Oscillator is a tool that measures momentum by looking at how the closing price of an asset relates to its price range over a set period. It is plotted on a chart as two lines, %K and %D. The %K line is more sensitive and volatile, while the %D line is smoother and less volatile.
When the %K line crosses above the %D line, it is considered a bullish signal, and when the %K line crosses below the %D line, it is considered a bearish signal. Divergence occurs when the Stochastic Oscillator and the price of the asset being traded move in opposite directions. This could indicate a possible reversal in the trend, suggesting that the current direction might be about to change as in case of RSI.
Identifying Divergence
Traders rely on divergence as a potent tool to spot potential shifts in trends and possible reversals. It occurs when the price of an asset and a technical indicator used to analyze the price movement move in opposite directions. In this section, we will explore the different types of divergence and how to identify them.
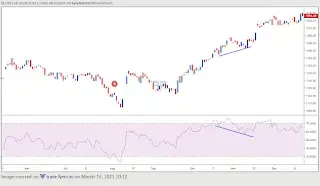
Bullish Divergence
Bullish divergence occurs when the price of an asset is in a downtrend, but the technical indicator used to analyze the price movement is showing higher lows. This indicates that the momentum of the downtrend is slowing down, and a potential trend reversal may be on the horizon. Traders can use this information to enter long positions or exit short positions.
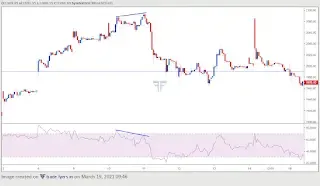
Bearish Divergence
Bearish divergence occurs when the price of an asset is in an uptrend, but the technical indicator used to analyze the price movement is showing lower highs. This indicates that the momentum of the uptrend is slowing down, and a potential trend reversal may be on the horizon. Traders can use this information to enter short positions or exit long positions.
Hidden Divergence
Hidden divergence occurs when the price of an asset is making higher highs or lower lows, but the technical indicator used to analyze the price movement is showing the opposite. This indicates that the momentum of the trend is continuing, despite the price movement suggesting otherwise. Traders can use this information to confirm the strength of the trend and make informed trading decisions.
Traders can identify divergence by comparing the price movement of an asset with a technical indicator, such as the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) or Relative Strength Index (RSI). They can also use chart patterns, such as Head and Shoulders or Double Tops, to identify potential divergence.
Bullish hidden divergence
Bearish hidden divergence
In conclusion, identifying divergence is a crucial skill for traders looking to make informed trading decisions. By understanding the different types of divergence and how to identify them, traders can enter or exit positions with confidence and increase their chances of success.
Divergence Trading Strategies
Divergence trading is a popular strategy used in technical analysis to identify potential trend reversals. In this section, we will discuss some common divergence trading strategies and how to use them effectively.
Entry and Exit Points
One of the key aspects of divergence trading is identifying the right entry and exit points. Traders typically look for divergences between price and an oscillator, such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI) or Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD). In a bullish divergence, the price drops to a new low while the oscillator goes for a higher low. On the flip side, a bearish divergence happens when the price reaches a higher high while the oscillator settles for a lower high. Traders leverage these signals to make decisions on when to enter or exit trades.
Risk Management
As with any trading strategy, risk management is crucial in divergence trading. Traders should always use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and protect profits. It is also important to use proper position sizing and not to risk too much on any one trade. Traders should also be aware of market conditions and adjust their risk accordingly.
Combining Indicators
Another effective way to use divergence trading is by combining multiple indicators. For example, traders can use both the RSI and MACD to confirm signals and increase the likelihood of a successful trade. By looking for divergences between multiple indicators, traders can improve their accuracy and reduce the risk of false signals.
Overall, divergence trading can be a powerful tool for identifying potential trend reversals and generating profits. However, it is important to use proper risk management and combine indicators effectively to increase the likelihood of success.
Limitations of Divergence Analysis
While divergence analysis is a useful tool in technical analysis, it is not without its limitations. Here are some of the key limitations of divergence analysis:
False Signals
One of the main limitations of divergence analysis is that it can produce false signals. This is because divergences can occur for a variety of reasons, not all of which are related to changes in price trends. For example, divergences can occur due to changes in market volatility, or due to changes in the underlying asset's fundamentals. As a result, traders should be cautious when using divergence analysis and should always confirm their findings with other technical indicators.
Lagging Indicators
Another limitation of divergence analysis is that it is a lagging indicator. This means that it can take some time for divergences to appear on the chart, and by the time they do, the price trend may have already changed direction. As a result, traders should use divergence analysis in conjunction with other technical indicators to confirm their findings and to avoid being caught out by sudden price reversals.
Not Suitable for All Assets
Divergence analysis is not suitable for all assets. It works best with assets that are highly liquid and have a high trading volume, such as major currency pairs and blue-chip stocks. It may not work as well with less liquid assets, such as penny stocks or thinly traded commodities. As a result, traders should consider the liquidity of the asset they are trading when using divergence analysis.
In conclusion, while divergence analysis is a useful tool in technical analysis, traders should be aware of its limitations and should use it in conjunction with other technical indicators to confirm their findings. By doing so, they can avoid false signals and make more informed trading decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can one identify divergence on a stock chart?
Divergence is identified by observing the relationship between the price of an asset and a technical indicator such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI). A bullish divergence occurs when the price of an asset is making lower lows, but the RSI is making higher lows. Indeed, a bearish divergence unfolds when the price achieves higher highs while the RSI simultaneously registers lower highs.
What does bullish divergence indicate for traders?
Bullish divergence is a signal that the price of an asset may be about to reverse its downward trend and begin to rise. This can be a good opportunity for traders to enter a long position and take advantage of the upward trend.
What are the implications of divergence in the forex market?
Divergence in the forex market can indicate a potential change in the direction of a currency pair's price trend. Positive divergence suggests a potential upward trend, while negative divergence suggests a potential downward trend.
Which indicators are best suited for spotting divergence?
There are several technical indicators that are commonly used to spot divergence, including the RSI, Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), and Stochastic Oscillator. Traders may use one or more of these indicators to identify divergence and make trading decisions accordingly.
Can divergence be considered a reliable signal for stock market trading?
While divergence can be a useful tool for traders, it is not always a reliable signal. Traders should use divergence in combination with other technical analysis tools and market data to make informed trading decisions.
How does one differentiate between types of divergence in trading analysis?
Divergence comes in two variations: bullish and bearish. Bullish divergence occurs when the price of an asset is making lower lows, but the technical indicator is making higher lows. Bearish divergence occurs when the price is making higher highs, but the technical indicator is making lower highs. Traders should be able to differentiate between the two types of divergence to make informed trading decisions.
Video shared below is from our channel share market Malayalam about hidden divergence. I have tried to explain it in simple language with chart example. Please check it for more chart examples.
Hidden divergence - https://youtu.be/MBiYSr1RIbM?si=33mQt0GzLUjljSsbposition sizing











0 Comments